Types of loan
Education Loan
“Education is the way out of the poverty trap. It shouldn't be the poverty trap itself and make those trying to better themselves incur massive student debt.”
personal Loan
"Our abode in this world is transitory, our life there in is but a loan, our breaths are numbered and our indolence is manifest."
Agriculture Loan
"Agriculture is our wisest pursuit, because it will in the end contribute most to real wealth, good morals & happiness."
Home Loan
“I believe that all of our lives we’re looking for home and if we’re really lucky, we find it in someone’s loving arms. I think that’ what life is-coming home.”
Features
Loans come with different features that can change the security of the loan, the payments on the loan, and the interest rate of the loan. The main features include secured versus unsecured loans, amortizing versus non-amortizing loans, and fixed-rate versus variable-rate (floating) loans.

Secured vs. Unsecured Loans
- Secured Loan Example
An example of a secured loan would be a mortgage where the borrower’s house is used as collateral and may be forfeited if the borrower is unable to pay their mortgage. - Unsecured Loan Example
An example of an unsecured loan would be a line of credit where the borrower is able to borrow money without using collateral.

Amortizing vs. Non-Amortizing
Amortizing
In amortizing loans, the principal payments are spread out over several periods, which means the principal amount on the loan will decrease with time.
Non-Amortizing
Non-amortizing loans require regular payments, but the payments do not include the principal balance. The principal is paid in full at the end of the loan period.
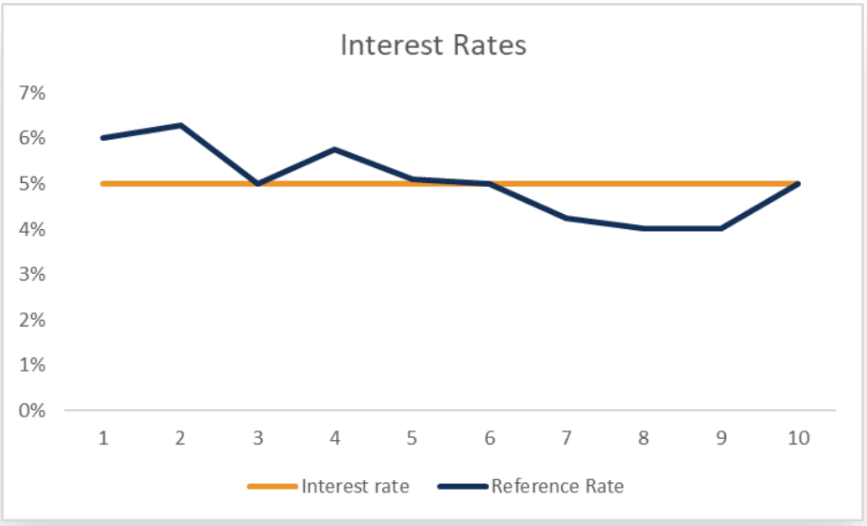
Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate (Floating)
- Fixed-Rate
Fixed-rate loans protect the borrower from rising interest rates since they won’t adjust upward if the reference rate were to increase. In addition, fixed-rate loans are worse for the borrower if the interest rate falls. - Variable-Rate (Floating)
A variable-rate loan protects the borrower from falling interest rates because the loan rate will adjust downward with the reference rate.

Tax Benefits
Certain Long Term loans with advances come with tax benefits. The best example is a Home Loan, where you can claim tax deductions of INR 150,000 under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, on the principal loan repayment. Similarly, you can avail of annual tax deductions of INR 200,000 on interest repayment under Section 24B.